Synchronization and desynchronization mechanisms
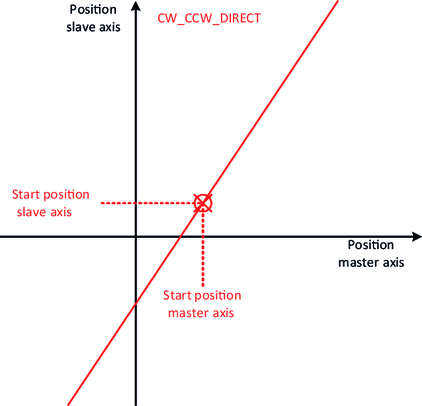
Synchronous operation is characterized by a linear positional relationship between the master and slave axis:
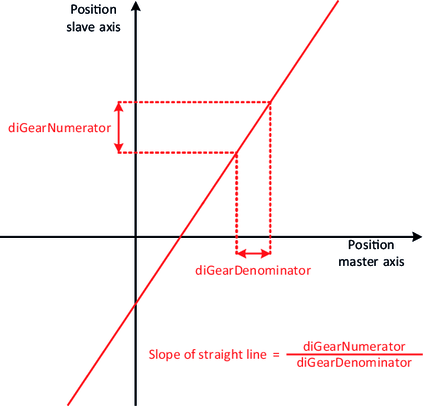
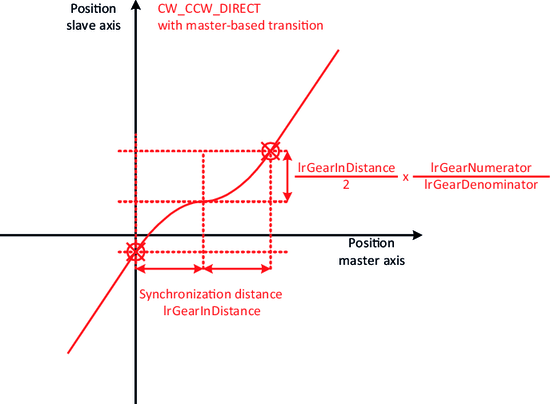
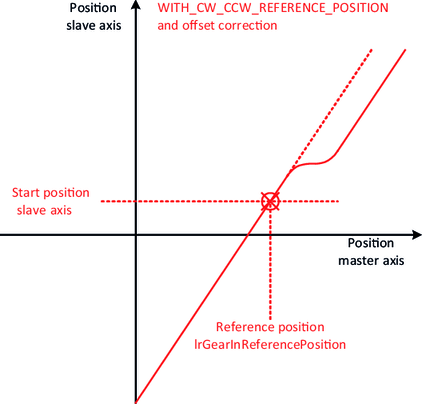
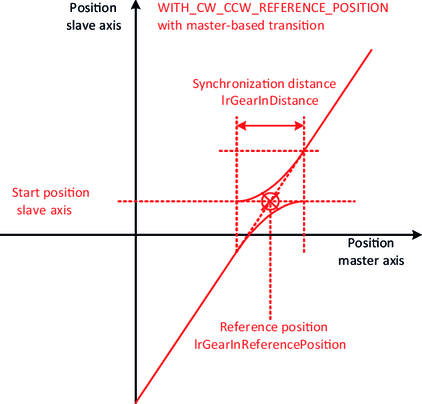
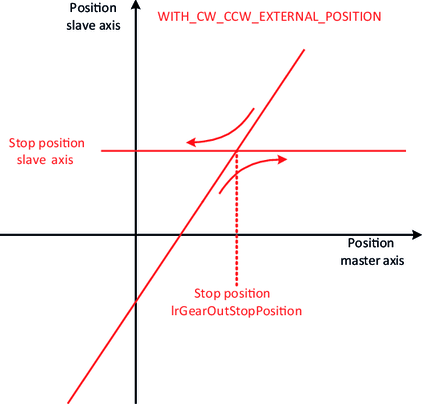
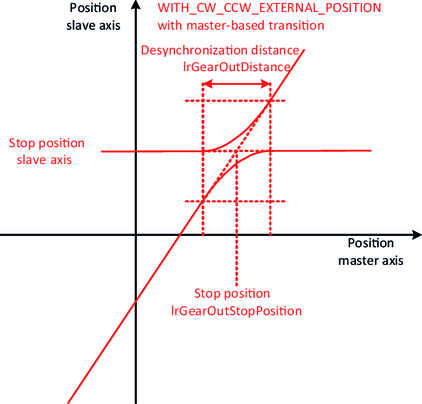
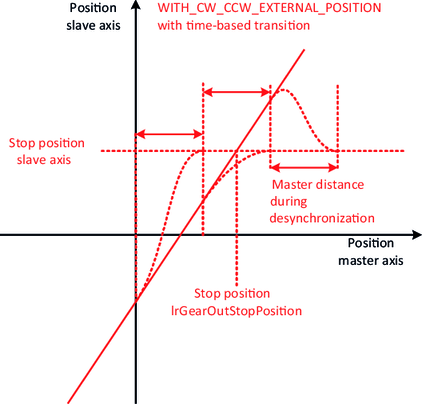
The slope of the straight lines can be specified using the variables diGearNumerator and diGearDenominator. To precisely define the lines, an "attachment point" is also required, which fixes the exact position of the lines in the plane. The various synchronization mechanisms serve this purpose.
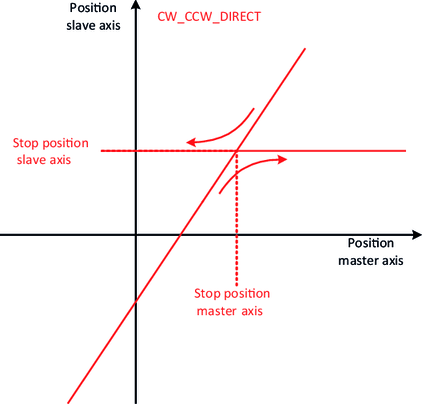
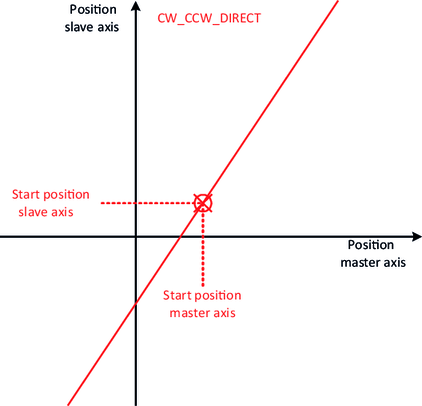
- In the case of the direct synchronization mechanism, the "attachment point" results from the current positions of the master axis and the slave axis.
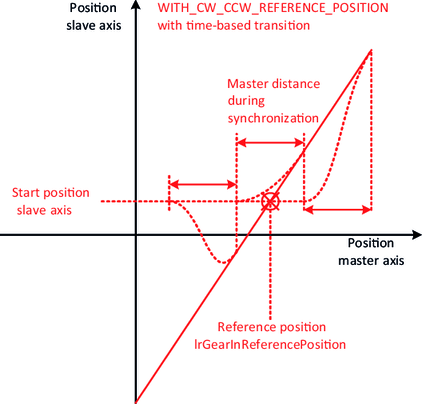
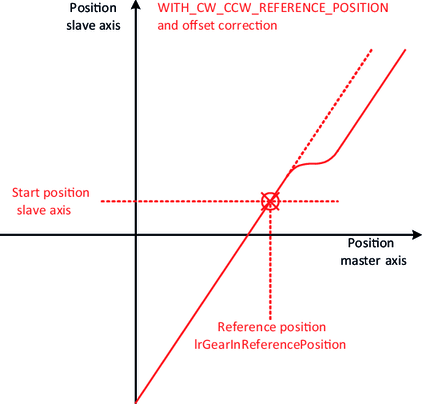
- In the case of the synchronization mechanism with a reference position, the "attachment point" results from the current position of the slave axis and the configured reference position IrGearInReferencePosition of the master axis.
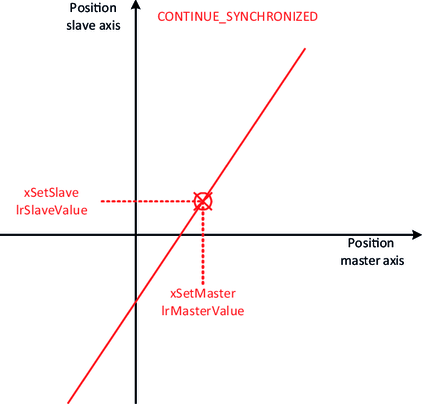
- In the case of the synchronization mechanism with a synchronous point, the "attachment point" results from the last position values for the master and slave axis saved in the "Gearing" mode. The master position can be set by the user with xSetMasterValue and IrMasterValue and the slave position can be set with xSetSlaveValue and IrSlaveValue.
Additional information