Powertrain for bidirectional travel
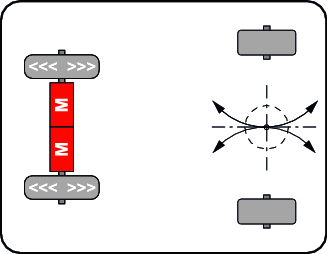
Differential powertrain
| With the differential drive, the vehicle is steered by speed differences of the two rigid drive wheels – similar to the principle of a chain vehicle. Swivel casters at the front and/or rear keep the system stable. Disadvantages include restrictions on maneuvering capabilities, load distribution and longer times required for complex maneuvers.
|
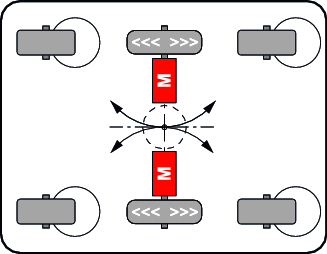
Differential powertrain with turntable drive
| With a differential powertrain with turntable drive, the drives of the turntable drive are installed on a slewing gear. The differential powertrain on the 2nd axis provides additional propulsive power and a more precise steering.
|
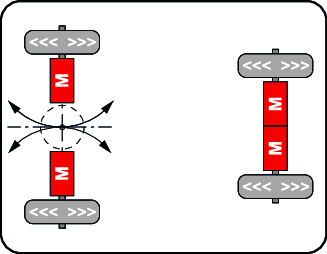
Powertrain with single-turntable drive
| With a single turntable drive, the drives are installed on a slewing gear. The slewing gear also has a position encoder. The rotary movement can occur at standstill or during travel. The turntable drive allows for small turning circles and smooth vehicle movement.
|
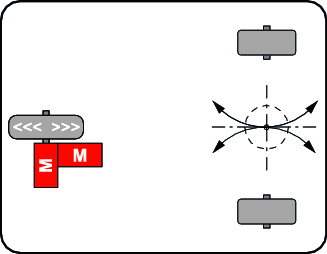
Travel/steering powertrain
| A travel/steering drive consists of a driven swivel caster and a steering drive. The load is distributed via two non-driven fixed casters.
|