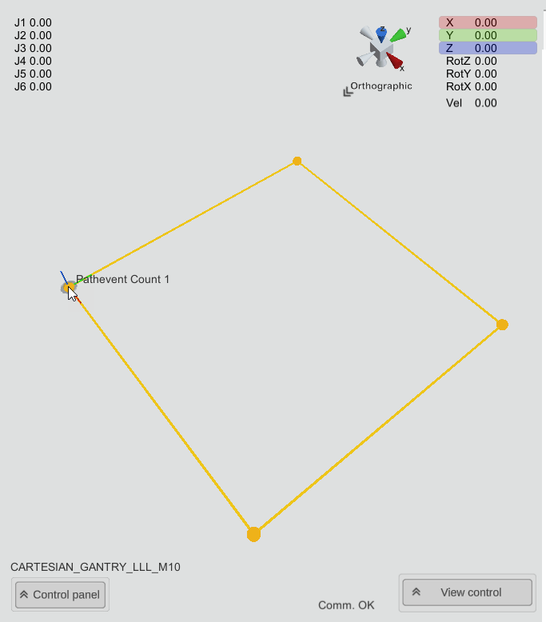
Example: Path events
INFORMATION
Make sure that all the required indices of the M-functions are implemented as an IEC call function in the user program before executing the G-code. Furthermore, the implemented IEC call function must return "TRUE" as a result during its first call in behavior 3 (path event). Otherwise, an error that will cause an emergency stop of the application will occur when the path event is triggered.
The following example shows the conversion of G-code to SEW Robot Language when all M-functions used have been configured with path event.
Observe the following information for this example:
- If there is no travel command between the end of the program (
END_PROG) and the end of a registered path event (REG_PATH_EVENT), the G-code import automatically adds an empty linear travel command (LIN_EXPLICITwithout coordinates). - The empty linear travel command is needed so that a path event is permissible at the end of the program. This causes the point that was last entered (via
X,Y,Z,A…) to be traveled to again and causes an exact stop. - If the imported G-code program is invoked as a sub-program via the SEW Robot Language command
CALL_PROGand the aforementioned situation applies to this G-code program, an exact stop will be performed before exiting the subprogram. Avoid registering a path event at the end of a subprogram if no exact stop is to be performed upon exiting.
G-code
G1 X0 Y0
M3
G1 X350
M4
G1 Y350
M5
G1 X0
M543
G1 Y0
M30
SEW Robot Language
|
Path events can be recorded using an activated pen (in the ControlPanel of the 3D simulation). A ball marks the position on the path, on which the M-function was executed or the path event was triggered.
|