Determining the overhung load
When determining the resulting overhung load, the type of transmission element mounted on the shaft end must be considered. The following transmission element factors fZ have to be considered for various transmission elements.
|
Transmission element |
Transmission element factor fZ |
Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Gear wheels |
1.15 |
< 17 teeth |
|
Sprockets |
1.40 |
< 13 teeth |
|
Sprockets |
1.25 |
< 20 teeth |
|
Narrow V-belt pulleys |
1.75 |
Consider influence of pretension force |
|
Flat belt pulleys |
2.50 |
Consider influence of pretension force |
|
Toothed belt pulleys |
1.50 |
Consider influence of pretension force |
|
Gear rack pinion, pretensioned |
2.00 |
Consider influence of pretension force |
|
Gear rack pinion, not pretensioned |
1.15 |
< 17 teeth |
Transmission element factor at low temperatures
For temperatures < -30 °C, observe a transmission element factor fZ1 = 1.2.
The overhung load applied to the motor or gear shaft is then calculated as follows:
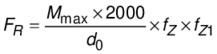
FR | Overhung load | [FR] = N |
Mmax | Torque in Nm | [Mmax] = Nm |
fZ | Transmission element factor |
|
fZ1 | Transmission element factor fZ1 = 1.2 for ambient temperatures < -30 °C. |
|
d0 | Overhung load determined by diameter of installed transmission element | [d0] = mm |
