Belly sway
- Configure the mechanical parameters of the application in the "Basic settings" area. The following figure illustrates the parameters available for this application type. For detailed descriptions of the parameters, refer to chapter Anti-sway control. The "Distance between lifting and traveling vehicle" is calculated by "Height of the tower" / 2, since the belly sway is greatest at this height. The value is used to determine the parameters of "Spring stiffness between tower and traveling vehicle" and the "Damping degree between tower and traveling vehicle". If you do not already know the "Spring stiffness between tower and traveling vehicle" and the "Damping degree between tower and traveling vehicle", e.g. from mechanical simulations, you can activate Support for parameter determination here.
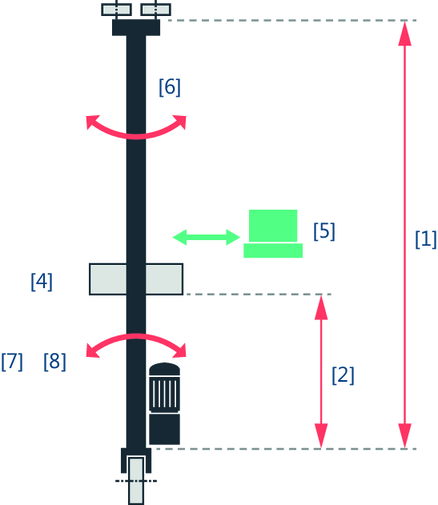
[1] | Height of the tower |
[2] | Distance between lifting and traveling vehicle (half lifting height) |
[4] | Mass of the lifting vehicle |
[5] | Mass of the payload |
[6] | Mass of the tower |
[7] | Spring stiffness between tower and traveling vehicle INFORMATION: To determine this parameter, see chapter Determining stiffness. |
[8] | Damping ratio between tower and traveling vehicle INFORMATION: To determine this parameter, see chapter Determining stiffness. |
- Define the effective lifting height by configuring the "Configured lifting height/offset" and the "Lifting height from fieldbus in mm" in the "Configuration of effective lifting height" area. The effective lifting height is calculated from the sum of these 2 parameters and describes the distance between the lifting and traveling vehicle on the basis of which the oscillation suppression is to be performed.
- Configured lifting height/offset: Fixed lifting height or an offset in [m]. This is often the lifting height with the strongest oscillation and thus equal to half the tower height.
- Lifting height of the fieldbus in mm: A value in mm can be specified via the fieldbus interface using the process data word "Distance between lifting and traveling vehicle". This means that, for example, variable lifting heights from external axes are taken into account.
- Specify the time window by configuring "Oscillation suppression" in the "Time window" area. The larger the time window, the more time is provided for the correction movement of the oscillation suppression and the dynamics of the correction signal is reduced. The positioning process is therefore extended by the time window. However, the jerk time of the travel axis can be reduced at the same time. A value is suggested for the parameter that you can apply and adjust, if necessary. The "Cycle time of the HighPrio task for limit value calculation" is also displayed in this area. The displayed value is drawn from the "Controller setpoint cycle" parameter of the lower-level member.