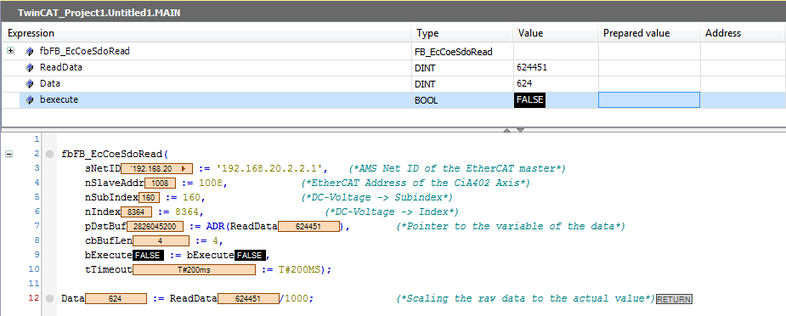
Example: Reading parameters
Parameters can be read using the READ SDO service. For this purpose, the index and subindex of the parameter to be read must be known.
The SDO service is described in detail in an example. In the example, the service is carried out in an EtherCAT® master from Beckhoff Automation GmbH in the TwinCAT 3 engineering tool.
Proceed as follows:
- You have integrated the required libraries and function blocks of the service for the EtherCAT® master in the TwinCAT project (see SDO services READ and WRITE).
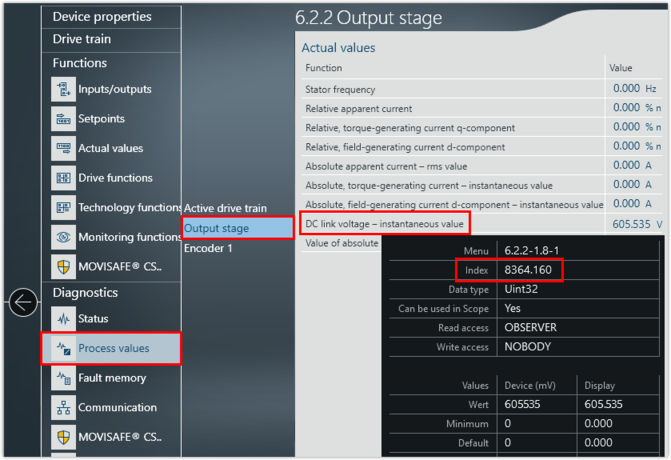
- Open the MOVISUITE® engineering software and search for the parameter.
- Move the mouse pointer over the edit box or display field of the parameter and note the index of the parameter from the tooltip. The subindex is separated from the index number by a dot.
- Create an instance of the
FB_EcCoeSdoReadfunction block. - Assign the inputs of the function block:
Input | Value |
|---|---|
sNetID | Net ID of the EtherCAT® master. |
nSlaveAddr | EtherCAT® address of the device from which data is to be read. |
nIndex | Index of the parameter that is to be read. When using a double-axis module, the index of the second axis is assigned with an offset of 0x1000 (4096 dec). |
nSubIndex | Subindex of the parameter that is to be read. |
pDstBuf | Pointer to the data range in which the read parameter is to be stored. |
cbBufLen | Maximum memory size in bytes occupied by the parameter to be read. For inverters of the MOVI-C® modular automation system, the maximum parameter memory size is always 4 bytes. |
bExecute | Positive edge that starts the read operation. |
tTimeout | Timeout time of the function block. |
- To start the process, the bExecute input must detect a "Rising Edge" (positive edge).
- The actual value of the parameter is displayed in the corresponding variable. The variable still needs to be scaled appropriately so that the actual unscaled value is displayed in the correct user units.
- In this example, the value of the DC link voltage was read out. You must scale the value with 1000.
- The bBusy and bError outputs signal the status of the SDO service. If an error occurs when running the SDO service and you have set the bError output, the nErrId output shows the error number.