Synchronizing directly with master-based transition
Transitions are usually used when the slave axis is to be synchronized with a moving master axis. To avoid a jump in speed, a transition function is used during synchronization.
Control the axis in the Gearing.Config.Start structure as follows:
Interface in the IEC Editor
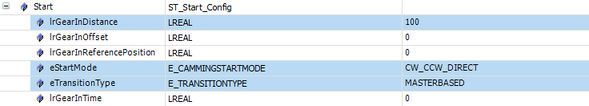
Procedure
- While the master axis is moving, the xStart start signal is set in the "Gearing" mode of the slave axis.
- With the configuration eStartMode = "CW_CCW_DIRECT" and eTransitionType = "MASTERBASED", the eGearingState state switches immediately from "STOPPED" (0) to "GEAR_IN" (2).
- After the master axis has traveled the configured synchronization distance lrGearInDistance = "100.0", the slave axis becomes synchronous. The eGearingState state switches from "GEAR_IN" (2) to "ACTIVE" (3).
- Then the master axis runs while the slave axis follows it.
Trace recording
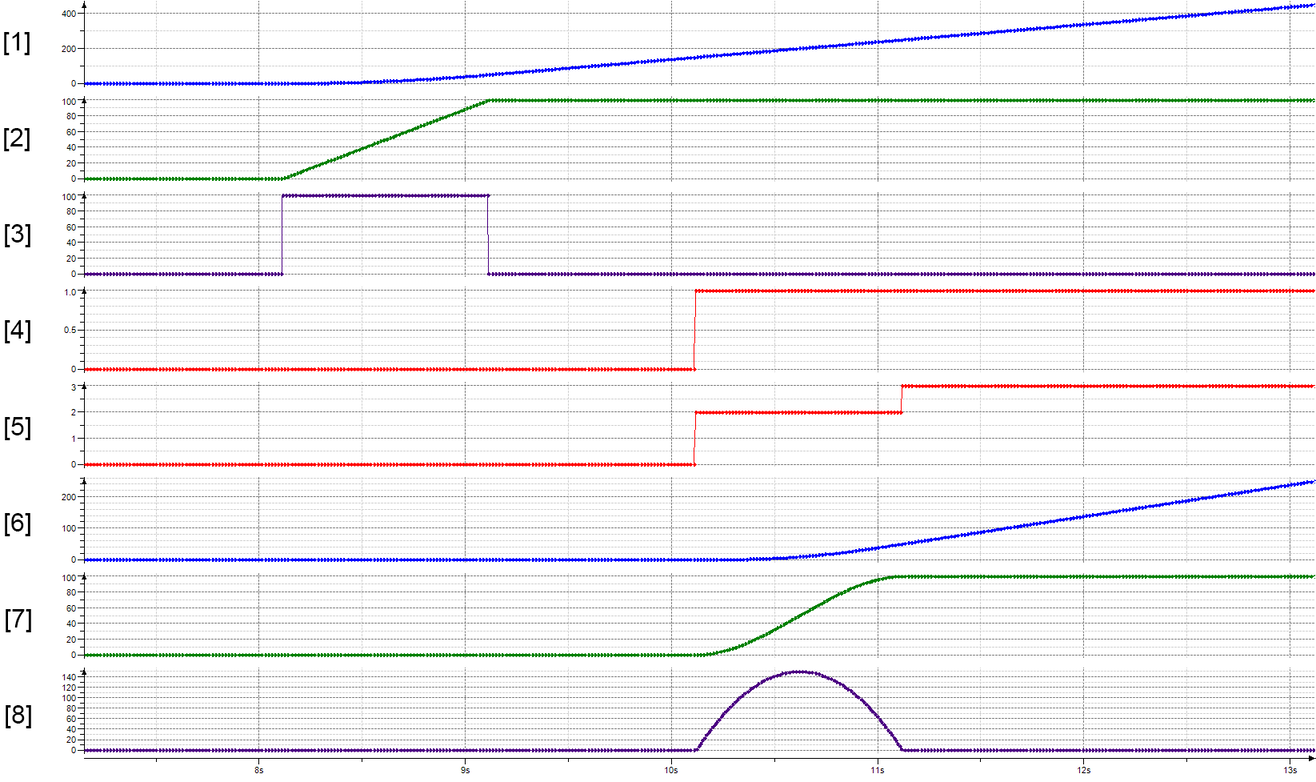
[1] | Position of the master axis |
[2] | Speed of the master axis |
[3] | Acceleration of the master axis |
[4] | xStart start signal of the Gearing mode |
[5] | eGearingState state of the Gearing mode |
[6] | Position of the slave axis |
[7] | Speed of the slave axis |
[8] | Acceleration of the slave axis |
A decisive factor for the master-based transition is that there must be a movement of the master axis for it to be performed. If the master axis is in the idle state, then the state "GEAR_IN" will remain until the master axis has traveled the configured synchronization distance.
Procedure
- While the master axis is in the idle state, the xStart start signal is set in the "Gearing" mode of the slave axis.
- With the configuration eStartMode = "CW_CCW_DIRECT" and eTransitionType = "MASTERBASED", the eGearingState state switches immediately from "STOPPED" (0) to "GEAR_IN" (2).
- This state is maintained until the master axis has traveled the configured synchronization distance lrGearInDistance = "100.0". Only then does the slave axis become synchronous. The eGearingState state switches from "GEAR_IN" (2) to "ACTIVE" (3).
Trace recording
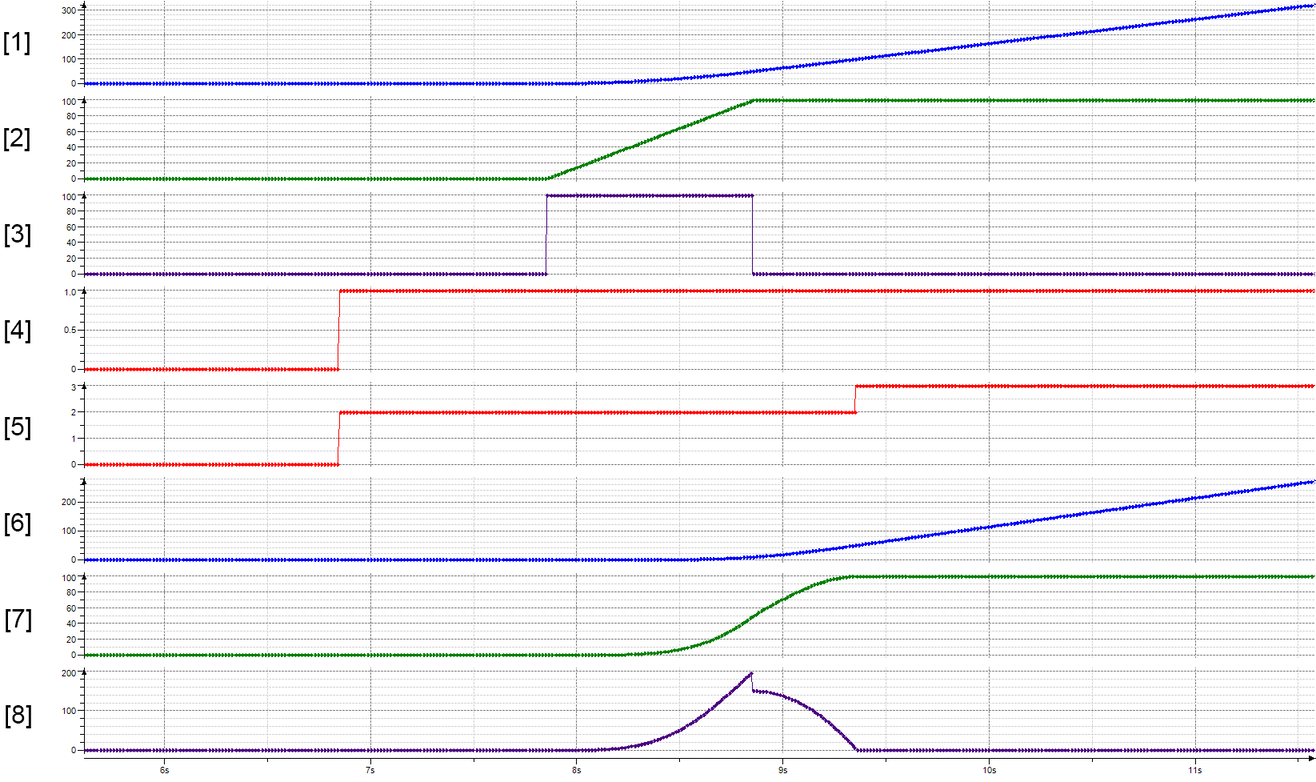
[1] | Position of the master axis |
[2] | Speed of the master axis |
[3] | Acceleration of the master axis |
[4] | xStart start signal of the Gearing mode |
[5] | eGearingState state of the Gearing mode |
[6] | Position of the slave axis |
[7] | Speed of the slave axis |
[8] | Acceleration of the slave axis |
