G-code
INFORMATION
A detailed description can be found in the ISO 6983-1 standard.
The G-code has established itself as a common language for programming machine tools (e.g. CNC machines). G-code can be used to define the course of paths and switch path-dependent actions using imperative programming. Apart from conventional programming, many CAD programs also enable you to generate the G-code from the available workpiece data. Even complex contours can in this way be represented as G-code programs.
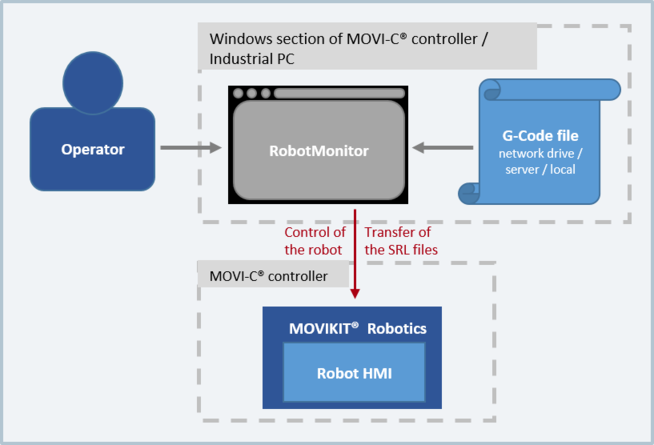
Unlike conventional numerical controls, G-code cannot be executed directly by the MOVI-C® CONTROLLER. However, since the SEW Robot Language supported by the software module is based on G-code, the G-code can be converted into the SEW Robot Language. The G-code file is imported, converted and transferred using the RobotMonitor and is manually executed as schematically shown in the following figure. For additional information, refer to chapter Manual G-code import/export.
G-code can also be imported automatically. The import is implemented via a function block in the IEC user program that controls the G-code converter, which is located on a Windows-based PC system. The import process is shown schematically in the following figure. For further information, refer to chapter Automatic G-code import.
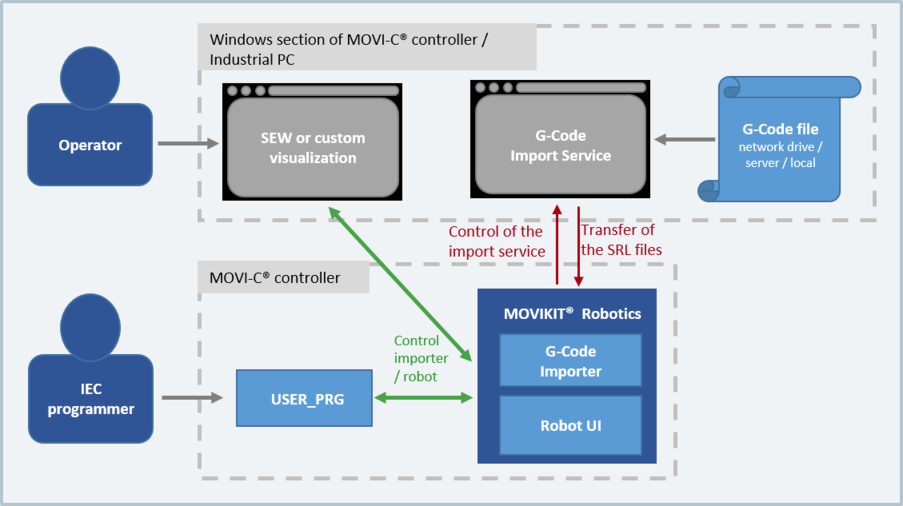
Before the import process, the programmer can decide on which program slot of the interpreter the converted G-code is saved. Subsequent editing or teaching of further motion commands is possible at any time in the RobotMonitor. RobotMonitor supports G-code programs that have been created according to ISO 6983-1 and in Siemens' Sinumerik dialect or Beckhoff's TwinCAT dialect. A G-code program can control exactly one robot instance.
For further information on this topic, refer to chapter Functional description.
